 What is the Dividend Yield Ratio?
What is the Dividend Yield Ratio?
Definition: Dividend yield is one of the measures investors who are seeking dividend income consider to decide on the company to invest in. The dividend yield ratio determines how much cash dividends each shareholder should receive relative to the current market value of each share. The ratio helps shareholders to determine ROI or estimated returns on their stock investment.
Usually, investors will invest in stocks with the expectation of earning returns through stock appreciation or dividend payments. Some companies will pay dividends regularly as a way of spurring investor interest. For most companies, the regular dividends offer some certainty about the stability of the company and for investors they are preferable because they are a source of steady income.
For companies that issue dividends, their stocks are considered income stocks. But some companies usually prefer reinvesting the money back into the company instead of paying dividends and such stocks are referred to as growth stocks.
Dividend Yield Formula
Dividend yield ratio formula is expressed as a percentage and it is determined by dividing dividends per share in a year by the market value of each share.
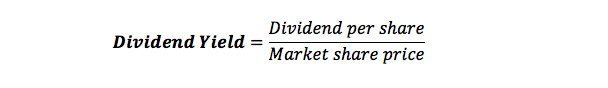
The value of dividends per share is provided in the financial statements of the company but sometimes they are represented in the form of gross dividends shared. You can calculate the dividend per share by dividing gross dividends shared by the total average shares.
You calculate the market value of the shares by taking the stock price as it appeared in the last session of the period or year from the stock exchange.
Dividend Yield Ratio Analysis
Using the dividend yield formula an investor can calculate how much returns they can receive at the end of the year from their stock investment. This means that they will be in a position to know the amount in dividends they will get from each dollar worth of the stock. The formula is very important for investors seeking to know if a stock’s dividend yield is increasing or declining. This is because is the company is giving out small dividends compared to its price then that is a sign for concern although some might be withholding more income rather than paying dividends.
Companies having a higher dividend yield ratio are likely to give out huge amounts in dividends compared to the current market value of each share. This is an indication of the high compensation of investors relative to low dividend yield stocks. However, sometimes a lower dividend yield can be favorable because it means the company is reinvesting most of the profits which are likely to increase the stock price in the future.
It is important to note that a low or high dividend yield depends on the industry or market the company is operating in. Tech companies are unlikely to give dividends and the earnings are reinvested in such growth stocks. Sometimes a small dividend is likely to return a higher dividend yield in the tech sector because after all investors are interested in high yields. The ideal dividend yield ratio should be between 3% and 4% and a ratio as high as 10% means that these are unsustainable levels and the company will cut the yields with time.
How to Calculate Forward Dividend Yield
Sometimes investors might be looking at future dividend earnings and thus they can calculate the forward dividend yield to help estimate returns.
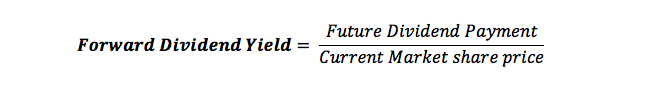
Summary
Generally, dividend-yielding stocks are considered to be stable and the ratio enables investors to gauge how the stocks are performing and the dividends they are paying overtime.
Investors should be wary of stocks that offer higher dividend yields in the first investment year but declines over time. For investors looking at income stocks, they should, therefore, look for stocks that are yielding consistent dividends with a higher ratio.
