 What is Days Sales in Inventory?
What is Days Sales in Inventory?
Definition: Days sales in inventory which is also referred to as days in inventory or days inventory outstanding is usually the period a company will take to convert its inventory into sales. A company’s total inventory includes the sum of progress payments, finished products as well as those in progress. In simpler terms, this financial ratio shows the number of days it will take the company to clear its stock.
The measure is very important to investors and creditors because it provides the company’s liquidity position, value as well as its cash flows. Usually, older inventory is more obsolete and could be less worth relative to fresh and current inventory. The ratio will help in determining the rate at which the company is moving inventory.
Companies will prefer to have low days sales in inventory ratio because it indicates its efficiency in operations and thus enhancing cash flow in the company. In contrast when the days sales in inventory are large or high then it means that the company has invested a lot in inventory relative to the rate of movement and that means that chances of products becoming obsolete in the market are high. Also if it takes longer to move inventory it will increase costs of storage as well as expose inventory to other risks such as theft and expiry of goods.
Days Sales in Inventory Formula
There are three versions of the DSI formula that you can use to calculate the ratio depending on what you are interested in.

Alternatively, you can calculate days sales in inventory formula like this:
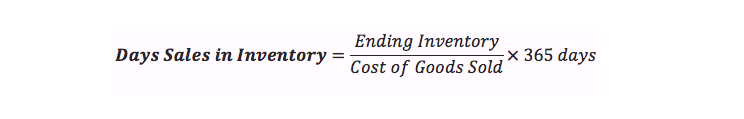
You can obtain the ending inventory from a balance sheet and this for a retail company includes finished goods. However, for companies with goods still in production, you have to include them to get accurate ending inventory.
Also, days sales in inventory can be determined through:
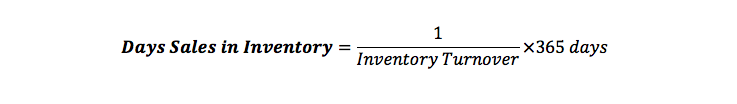
In this formula, you use inventory which is how many times the company stocks in the course of that period like say a year. Inventory turnover is calculated by dividing the total cost of sales by average inventory. Usually, a year will have 365 days but sometimes you can use 360 days.
Days Sales in Inventory (DSI) Example
The formulas above give a way of calculating days sales in inventory depending on their accounting practice. The ratio is very important in that it informs on how long the stock can stay in the stores.
Therefore it is beneficial in ensuring that there is a faster movement of inventory to enhance cash flows and minimize storage costs. If inventory stays on the shelves longer then it means cash is tied and it is unavailable for the company’s other operation this costing it more money.
Days Sales in Inventory Analysis
The days sales in inventory value are important in demonstrating the company’s efficiency. If the DSI value is low then it means the operations of the company are efficient since it takes a short time to clear inventory and then restock or put that money in other operations. It is ideal to have a low DSI because it ensures the company cuts of storage cost. Equally when dealing with perishable goods clearing inventory faster guarantees that customers can receive fresh products and minimize the chance of losses from goods expiring.
You should not compare the DSI values of different companies operating in different industries because the value differs according to industry. Always use it to compare companies operating in the same sector.
Summary
The days sales inventory ratio helps in informing the company on the average time it will to clear inventory and thus it is vital in determining the efficiency of the company’s operations. A low DSI is preferable because it shows that the company is managing inventory properly.
